KOREAN ENGLISH
주요취급품목
PolyWAX LPTM
PolyGLYCOPLEX ATM
PolyHYDROXYETHYL ATM
SDS Removal
PolyMETHYL ATM
PolyPROPYL ATM
TopTipsTM/Nu TipsTM
분취용 HPLC컬럼
Flash Cartridges
Flash LC 시스템
Detectors
Chromatography Gels
Hydrophilic
Interaction Chromatography (HILIC)
This is a variant of normal phase
chromatography that is performed with a very polar stationary phase and a
mostly organic mobile phase. When the mobile phase contains > 60% organic
solvent, then hydrophilic interaction becomes significant. With neutral
materials such as PolyHYDROXYETHYL A™, this is the only significant
force involved. With ion-exchange columns, hydrophilic interaction will be
superimposed on the electrostatic effects. See the example of this with Histone H1 phosphorylation variants.
Order PolyHYDROXYETHYL A™ now.
Selectivity in HILIC is the opposite of
that of RPC. It is very sensitive to addition or deletion of a Ser- or
carbohydrate residue, less sensitive to addition or deletion of a Leu- or Phe-
residue. Thus, the two modes are complementary and are sometimes used in
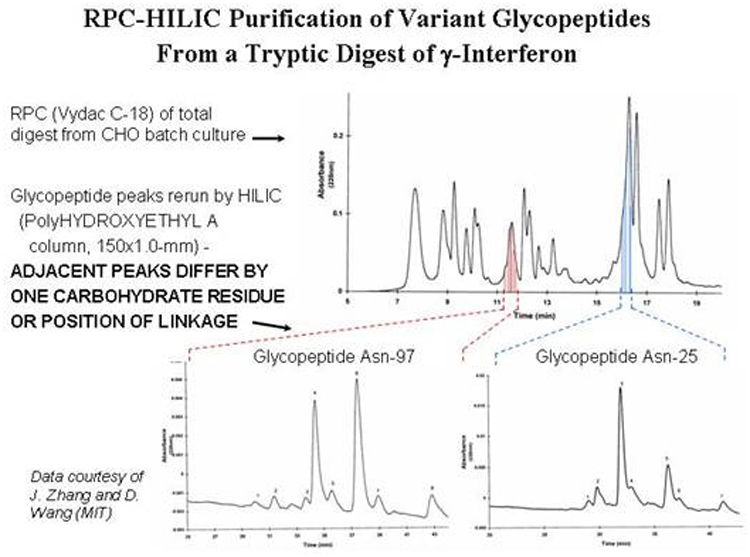
sequence to purify complex mixtures. An example is the assessment of the degree
of glycation of γ-interferon. The tryptic fragments are resolved on a RPC
column. The two glycopeptide peaks are collected and rerun via HILIC on a
PolyHYDROXYETHYL A™ column. This resolves each peak into a library of
glycopeptide peaks, each differing from its neighbor by one carbohydrate
residue.
Basic residues are the most hydrophilic,
followed by phosphorylated residues. Next comes Asn-, Ser-, etc. with Phe- and
Leu- being the least hydrophilic.
The more polar a stationary phase, the
less organic solvent necessary to get a given degree of retention. PolyHYDROXYETHYL
A™ was designed to afford superior results in HILIC. Select the pore
diameter that matches your application:
1) 60- or 100-Å: Small solutes in general.
See Metabolomics. The
3-µm, 100-Å material is particularly useful.
2) 200- or 300-Å: Peptides and most proteins; di- and trinucleotides (ADP;
NADH; etc.)
3) 1000-Å: Extremely polar solutes such as ATP and aminoglycoside antibiotics
(see Metabolomics).
Salts: Essential to get reproducible retention
times and symmetrical peaks. Usually, 10-15 mM suffices unless the solute is
highly charged. Ammonium acetate or formate can be used if salt must be
volatile. If the absorbance is to be monitored at low wavelengths such as 215
nm, then use triethylamine phosphate (TEAP) or sodium methylphosphonate. In
cases where the solute is extremely well retained, such as intact proteins, try
50 mM formic acid as the additive.
pH: Retention of peptides is maximal around
pH 3. This is because they have a net + charge at that pH, and basic solutes
are the most polar. Solutes that are not electrolytes are less sensitive to pH.
NOTE: Selective isolation of glycopeptides: Dr. Steven Carr (Broad
Institute) has observed that glycopeptides can be isolated from a tryptic
digest with reasonable selectivity by HILIC on a PolyHYDROXYETHYL A™
column (e.g., item# 202HY0503) with a decreasing ACN gradient and 15 mM
ammonium acetate right out of the bottle (pH ~ 6.5). This seems to reflect the
fact that retention due to the peptide moiety decreases from pH 3 to pH 6.5,
while retention due to the glycan moiety is relatively unaffected. Thus, the
contribution of the glycan to retention is a greater percentage of the total,
and glycopeptides elute as a class immediately after the nonglycopeptides.
Solvents: ACN and PrOH afford comparable
retention. Backpressure is lower with ACN, while PrOH is a better solvent for
intact proteins. An ACN:PrOH blend seems to be an even better solvent for
proteins. BuOH affords even better retention than do these solvents, but its
high viscosity limits the amount that can be employed.
Intact proteins: While water-soluble proteins such
as cytoplasmic enzymes do not lend themselves well to HILIC, HILIC works well
for proteins that do not normally occur free in aqueous solution, such as
membrane proteins and histones. See Proteomics.
PolyHYDROXYETHYL
A™ is a trademark of PolyLC Inc. All Rights Reserved
주소
서울특별시 송파구 충미로 5 송파한화오벨리스크 C동 415호
연락처
전화번호 : 02-3012-9003 팩스번호 : 02-3012-9010
intertech9@naver.com
사업자등록번호
215-87-83507 대표이사 : 이홍근
